Your Dominant negative mutation example images are ready in this website. Dominant negative mutation example are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Dominant negative mutation example files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for dominant negative mutation example pictures information linked to the dominant negative mutation example interest, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our website always provides you with hints for downloading the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Dominant Negative Mutation Example. Combined immunodeficiency and atopy caused by a dominant negative mutation in caspase activation and recruitment domain family member 11 CARD11. Say you have protein receptor X. These are called dominant negative mutations. Typical examples of dominant-negative mutations.
 Bil 250 Lecture 7 From bio.miami.edu
Bil 250 Lecture 7 From bio.miami.edu
The ability of RNAi to phenocopy or enhance a dominant mutation would suggest that the mutation is a dominant negative although a negative result in this case is difficult to interpret. Dominant-negative effects have been related to proteins involved in signaling and transcriptional activity. A dominant negative effect may occur as a result of mutations that abrogate the activity of proteins that multimerize either with themselves or with other binding partners. A human example is cystic fibrosis. These are called dominant negative mutations. Combined immunodeficiency and atopy caused by a dominant negative mutation in caspase activation and recruitment domain family member 11 CARD11.
Harmful mutations may cause genetic disorders or cancer.
A mutation in a single gene causes the body to produce thick sticky mucus that clogs the lungs and blocks ducts in digestive organsMar 5 2021. Also as compared to recessive mutations or wild-type p53 dominant negative mutations are associated with an earlier age of onset in patients with sporadic glioblastoma Marutani et al 1999. What is an example of a negative mutation. A dominant negative mutation in a nutshell is basically a heterozygous mutation one normal gene producing normal protein and one mutated gene producing mutant protein where the mutant protein inhibits the actions of the normal protein In your example the mutant Tx factor inhibits the actions of the normal Tx factor by binding to the DNA and blocking the. A specific example is provided by Drosophilas dorsal dl proteins DNA binding activity which depends on dimerization. These are called dominant negative mutations.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The result of a negative mutation is a non-sense protein. For example distinguishing dominant negatives from dominant gain of function alleles may be difficult in a vacuum. The ability of RNAi to phenocopy or enhance a dominant mutation would suggest that the mutation is a dominant negative although a negative result in this case is difficult to interpret. What is the Difference Between Haploinsufficiency and Dominant NegativeHaploinsufficiency occurs when only a single copy of the gene is functional while dominant negative occurs when the mutant polypeptide reduces the activity of the co-expressed wild type protein. Marfan syndrome is also an example of dominant negative mutation and haploinsufficiency.
 Source: bio.miami.edu
Source: bio.miami.edu
A genetic disorder is a disease caused by a mutation in one or a few genes. Dämənənt negədiv myütäshən cell and molecular biology Mutation resulting in a gene product that can interfere with the function of the normal gene product in heterozygotes. Examples of negative mutations includea frame shift mutation - codons are. Molecular biologists are increasingly faced with the problem of assigning a function to genes that have been cloned. STAT3 dominant-negative disease STAT3DNalso known as autosomal dominant hyper-IgE syndrome AD-HIES or Jobs Syndromeresults from mutations in the gene that encodes a signaling protein called STAT3.
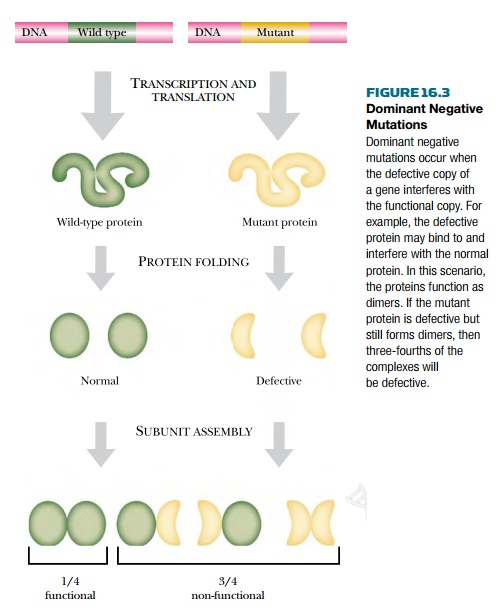
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
What is an example of a negative mutation. Dominant negative mutants have already provided insights into the molecular mechanisms of action of a number of protein families including hormone receptors oncogenes and growth factor receptors and have been identified as the cause of. A mutation could be a loss-of-function or gain-of-function mutation depending on whether the gene product is inactivated or has enhanced activity. Marfan syndrome is also an example of dominant negative mutation and haploinsufficiency. In heterozygotes with two copies of every allele some mutated gene products can suppress the effect of the wild-type allele.
 Source: sci.sdsu.edu
Source: sci.sdsu.edu
Say you have protein receptor X. A new approach to this problem involves the manipulation of the cloned gene to create what are known as dominant negative mutations. Marfan syndrome is also an example of dominant negative mutation and haploinsufficiency. A mutation whose gene product adversely affects the normal wild-type gene product within the same cell. A human example is cystic fibrosis.
 Source: differencebetween.com
Source: differencebetween.com
What is an example of a negative mutation. In heterozygotes with two copies of every allele some mutated gene products can suppress the effect of the wild-type allele. Dominant mutations may be positive or negative Occasionally a mutation causes a change of function or even a gain of function in the resulting gene product. What is an example of a negative mutation. Usually hypomorphic mutations are recessive but haploinsufficiency causes some alleles to be.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
A human example is cystic fibrosis. What is an example of a negative mutation. Usually hypomorphic mutations are recessive but haploinsufficiency causes some alleles to be. A dominant-negative mutation may arise in a human somatic cell and provide a proliferative advantage to the mutant cell leading to its clonal expansion. A genetic disorder is a disease caused by a mutation in one or a few genes.
 Source: sci.sdsu.edu
Source: sci.sdsu.edu
Dominant negative mutations are characterized by a dominant or semi-dominant phenotype and usually result in loss of function. Dominant negative mutations are characterized by a dominant or semi-dominant phenotype and usually result in loss of function. A human example is cystic fibrosis. A mutation could be a loss-of-function or gain-of-function mutation depending on whether the gene product is inactivated or has enhanced activity. A mutation whose gene product adversely affects the normal wild-type gene product within the same cell.
 Source: bio.miami.edu
Source: bio.miami.edu
A genetic disorder is a disease caused by a mutation in one or a few genes. What is the Difference Between Haploinsufficiency and Dominant NegativeHaploinsufficiency occurs when only a single copy of the gene is functional while dominant negative occurs when the mutant polypeptide reduces the activity of the co-expressed wild type protein. Molecular biologists are increasingly faced with the problem of assigning a function to genes that have been cloned. A mutation in a transcription factor that removes the activation. Although Herskowitz definition referred basically to intralocus interactions it is now recognized that interlocus eg trans-acting interactions can also lead to dominance Omholt et al 2000.
 Source: bio.miami.edu
Source: bio.miami.edu
Combined immunodeficiency and atopy caused by a dominant negative mutation in caspase activation and recruitment domain family member 11 CARD11. In this case the mutant protein affects the activity of every protein complex that it is integrated into thus causing more than a 50 decrease in that proteins activity. What is the Difference Between Haploinsufficiency and Dominant NegativeHaploinsufficiency occurs when only a single copy of the gene is functional while dominant negative occurs when the mutant polypeptide reduces the activity of the co-expressed wild type protein. A human example is cystic fibrosis. STAT3 dominant-negative disease STAT3DNalso known as autosomal dominant hyper-IgE syndrome AD-HIES or Jobs Syndromeresults from mutations in the gene that encodes a signaling protein called STAT3.
 Source: bio.miami.edu
Source: bio.miami.edu
Dominant mutations may be positive or negative Occasionally a mutation causes a change of function or even a gain of function in the resulting gene product. These are called dominant negative mutations. A mutation in a single gene causes the body to produce thick sticky mucus that clogs the lungs and blocks ducts in digestive organsMar 5 2021. Dominant negative mutations also called antimorphic mutations have an altered gene product that acts antagonistically to the wild-type allele. These encode mutant polypeptides that when overe.

Although Herskowitz definition referred basically to intralocus interactions it is now recognized that interlocus eg trans-acting interactions can also lead to dominance Omholt et al 2000. These are called dominant negative mutations. In this case a single mutant copy of the gene may cause significant phenotypic. Dominant negative mutations also called antimorphic mutations have an altered gene product that acts antagonistically to the wild-type allele. Dominant negative mutants have already provided insights into the molecular mechanisms of action of a number of protein families including hormone receptors oncogenes and growth factor receptors and have been identified as the cause of.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
A new approach to this problem involves the manipulation of the cloned gene to create what are known as dominant negative mutations. Combined immunodeficiency and atopy caused by a dominant negative mutation in caspase activation and recruitment domain family member 11 CARD11. A human example is cystic fibrosis. Herskowitz 1987 provided the classical definition of dominant-negative DN mutations as those leading to mutant polypeptides that disrupt the activity of the wild-type gene when overexpressed. These mutations usually result in an altered molecular function often inactive and are characterized by.
 Source: differencebetween.com
Source: differencebetween.com
Herskowitz 1987 provided the classical definition of dominant-negative DN mutations as those leading to mutant polypeptides that disrupt the activity of the wild-type gene when overexpressed. In this case the mutant protein affects the activity of every protein complex that it is integrated into thus causing more than a 50 decrease in that proteins activity. Hypomorphs after Mullerian classification are characterized by altered gene products that acts with decreased gene expression compared to the wild type allele. For example distinguishing dominant negatives from dominant gain of function alleles may be difficult in a vacuum. What is an example of a negative mutation.

A genetic disorder is a disease caused by a mutation in one or a few genes. Harmful mutations may cause genetic disorders or cancer. Dämənənt negədiv myütäshən cell and molecular biology Mutation resulting in a gene product that can interfere with the function of the normal gene product in heterozygotes. For example distinguishing dominant negatives from dominant gain of function alleles may be difficult in a vacuum. A dominant negative effect may occur as a result of mutations that abrogate the activity of proteins that multimerize either with themselves or with other binding partners.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
A dominant-negative mutation may arise in a human somatic cell and provide a proliferative advantage to the mutant cell leading to its clonal expansion. Marfan syndrome is also an example of dominant negative mutation and haploinsufficiency. Dominant mutations may be positive or negative Occasionally a mutation causes a change of function or even a gain of function in the resulting gene product. Also as compared to recessive mutations or wild-type p53 dominant negative mutations are associated with an earlier age of onset in patients with sporadic glioblastoma Marutani et al 1999. A dominant-negative mutation usually means that the resulting protein is has lost a certain part of its function negative but it can out-compete the endogenous protein in some way dominant.
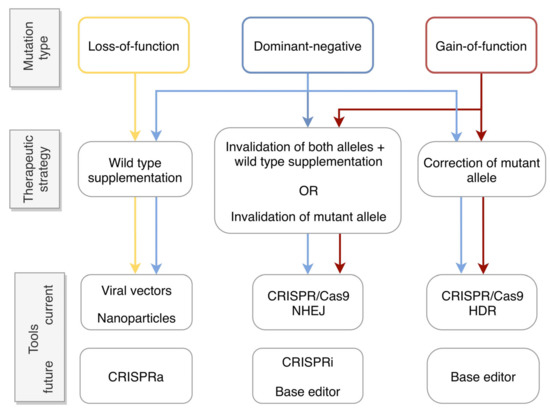
 Source: brainkart.com
Source: brainkart.com
What is an example of a negative mutation. These are called dominant negative mutations. Herskowitz 1987 provided the classical definition of dominant-negative DN mutations as those leading to mutant polypeptides that disrupt the activity of the wild-type gene when overexpressed. For instance a dominant-negative mutation in a gene necessary for the normal process of programmed cell death Apoptosis in response to DNA damage can make the cell resistant to apoptosis. Typical examples of dominant-negative mutations.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Examples are dominant negative mutations DNMs in which a defective subunit poisons a mac-romolecular complex. Dominant-negative effects have been related to proteins involved in signaling and transcriptional activity. A human example is cystic fibrosis. In this case the mutant protein affects the activity of every protein complex that it is integrated into thus causing more than a 50 decrease in that proteins activity. A genetic disorder is a disease caused by a mutation in one or a few genes.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Dominant negative mutants have already provided insights into the molecular mechanisms of action of a number of protein families including hormone receptors oncogenes and growth factor receptors and have been identified as the cause of. For example distinguishing dominant negatives from dominant gain of function alleles may be difficult in a vacuum. A genetic disorder is a disease caused by a mutation in one or a few genes. Herskowitz 1987 provided the classical definition of dominant-negative DN mutations as those leading to mutant polypeptides that disrupt the activity of the wild-type gene when overexpressed. The result of a negative mutation is a non-sense protein.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title dominant negative mutation example by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






